Alcoholism and drug addiction can cause premature death by overdose, damage to the body, or accidents caused by impaired judgment. Sniffing glue or hairspray can cause sudden death.
Innovative, personalized consultation for treatment of alcoholism and drug addiction.
Something went wrong. Please try again later.
Many substances can be abused. They are often taken for non-medical reasons, such as an athlete taking corticosteroids or growth hormones or anorexic ingesting laxatives.
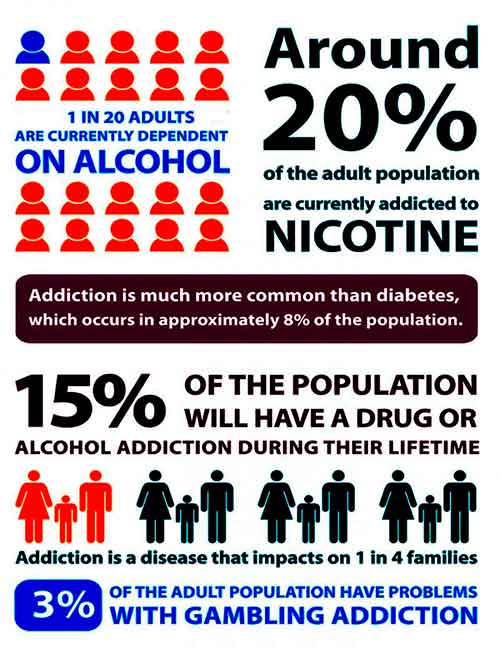
It should be noted that alcohol and drug addiction is also very dangerous as well as a gambling addiction. Moreover, usually alcohol, gambling, and drug addiction are related to each other.
Risk Factors
Alcoholism
- Men
- Family history
Substance abuse
- Aggressive behavior
- School failure
- Dropping out of school
- Family history of alcohol or drug abuse
Alcoholism
Alcoholism is when drinking affects physical or mental health, social relationships, family, or work. It is a disease. Dependence is a physical addiction to alcohol, with the appearance of withdrawal symptoms when consumption is reduced or stopped, and a growing tolerance, i.e. the need to ingest larger quantities of alcohol before feeling its effects.
In the case of alcohol abuse, the patient becomes a “binge drinker” without yet reaching the stage of physical dependence. Alcohol distorts judgment, impairs concentration, irritates the lining of the esophagus and stomach, slows the absorption of vitamins, triggers the liver disease, affects the heart muscle, and causes nerve damage, memory loss, birth defects such as fetal alcohol syndrome, sexual problems such as erectile dysfunction, and loss of menstruation.
In addition, alcoholism increases the risk of cancer of the larynx, esophagus, liver, and colon.
Addiction
Many substances can be addictive and cause serious health problems, including in young people.
The most common hallucinogens are LSD, mushrooms, mescaline, phencyclidine (“angel dust” or “PCP”), and ketamine (or “special K”). These drugs cause euphoria and lower inhibitions but lead to torpor, perceptual changes, paranoia, hallucinations, psychosis, and even death.
Cocaine is highly addictive. It triggers feelings of intense euphoria, greater self-confidence, and increased energy, and lowers inhibitions.
Methamphetamines and ecstasy make you feel euphoric, increase your energy, increase your stamina and alertness and lower your inhibitions. They increase blood pressure and heart rate, and can cause heart attacks and strokes in young, healthy people.
Heroin and other opiates, some of which are legally available as prescription painkillers, relieve pain, make you feel euphoric and can increase sexual pleasure.
But addiction sets in very quickly and larger amounts of the substance are needed to be effective. Physical problems and overdose can occur. Withdrawal requires medical follow-up.
Causes
Family history plays a major role. Children of alcoholics or drug addicts are more likely to develop an addiction.
Depression and other mental disorders can lead to the overuse of alcohol or drugs. Low self-esteem, relationship conflicts, or anxiety, combined with peer influence and stressful life, can also be triggers.
Prevention
Drug problems have increased dramatically in recent years, especially among youth. In the United States, studies have shown that one dollar invested in prevention generates a ten dollar savings in addiction treatment.
Often, families tend to deny substance abuse problems. Some family-based prevention programs aim to strengthen family bonds by increasing communication, involving parents more, providing information about addiction and substance abuse, and offering a moderate but consistent setting.
Prevention should begin in kindergarten with a focus on specific risk factors (behavior modification, poor social skills, and academic difficulties).
Development of self-control, emotional awareness and communication skills, social problem solving, and academic and psycho-emotional support could be addressed.
The media and various associations should serve as relays. Peer influence, a very important factor in high school, should also be integrated.
Interactive methods such as discussion groups and role-playing sessions in which children play the role of parents are effective in informing young people about the risks of alcohol and drug abuse and in promoting refusal to use harmful substances.
Diagnosis
The interference of alcohol or other substances with social relationships and work is a real problem.
Excessive drinking” is defined as having 15 or more drinks per week for women and 22 or more drinks for men, or at least six drinks on one occasion on a regular basis.
In practice, drinks are counted so that they contain the same amount of pure alcohol. A “glass” is, therefore, a unit equivalent to 10 cl of wine at 12°, 25 cl of beer at 5°, or 2.5 cl of spirits at 45°.
Coffee, tobacco, alcohol, and painkillers are commonly consumed substances, sometimes in excess. Depression and anxiety are more likely to lead to alcoholism or drug addiction.
Various tests identify the presence of drugs or alcohol in the body but do not define the existence of addiction. The diagnosis is made on the basis of symptoms triggered by drug use.
Other tests, such as liver function tests, blood counts, serum magnesium, uric acid, and total protein and folic acid levels will reveal the damage caused by alcoholism.
Treatments
Treatment for alcohol and drug addiction often combines medication and psychotherapy. Physical withdrawal symptoms should be treated first. Long-term treatment increases the chances of success
People who have undergone treatment for three months or more have had better results.
Detoxification
Stopping substance use abruptly can lead to withdrawal symptoms or physical withdrawal.
A detoxification program, either in a hospital or in an appropriate facility, must be implemented. In the case of alcoholism, delirium tremens can be fatal if not treated.
Medications
Several drug treatments help reduce withdrawal symptoms, suppress dependence on the substance, and block its effects.
Disulfiram causes unpleasant side effects when interacting with alcohol and promotes abstinence. Methadone is a substitution treatment for opiate addictions such as heroin and prevents the onset of withdrawal symptoms. Doses of methadone or other substitutes are gradually reduced, although some people may need to stay on methadone for months or even years.
There is no treatment for cocaine and ecstasy addictions, but medication can be used to treat the seizures and psychotic reactions that sometimes result from their use.
Psychotherapy
There are several types of therapies that help patients stay alcohol and drug-free. CBT teaches how to think and act to avoid using drugs.
Contingency planning uses a system of punishments and rewards to make abstinence more appealing than drug use. Psychoanalysis can also be helpful.
Vocational Training and Rehabilitation
Vocational skills are an essential part of getting the patient back to work and not relapsing.
Detoxification
It may be helpful to attend a rehab program (from a few weeks to several months) in a suitable facility.


